
In the realm of digital interactions, a subtle exchange often goes unnoticed. This section delves into the intricate dynamics where convenience in the virtual world comes at a concealed expense. It explores the mechanisms through which user engagement is subtly transformed into a commodity, impacting our digital experiences in profound ways.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Every click, search, and interaction online contributes to a vast pool of data. This data, though seemingly innocuous, plays a pivotal role in shaping the economic landscape of the internet. It’s crucial to recognize how this information is leveraged, influencing not just the content we encounter but also the security of our digital identities.
The value of Anonymity: As we navigate through the digital maze, the erosion of anonymity is a significant concern. This loss not only affects our perceived privacy but also impacts our ability to engage freely without external influence. The balance between utility and privacy is delicate, and understanding its implications is essential for maintaining a healthy digital ecosystem.
The Hidden Cost of Free Online Services

In this section, we delve into the underlying expenses that users unknowingly bear when utilizing ostensibly complimentary digital platforms. While these services may not charge directly for access, they often extract a different kind of payment–one that involves the utilization of user activity and preferences. This trade-off, though subtle, has significant implications for the digital consumer.
To better understand this phenomenon, it is crucial to explore the mechanisms through which these platforms generate revenue without direct user fees. Typically, this involves the collection and analysis of user data, which is then leveraged to tailor advertisements or to sell to third parties. Below is a table that outlines common methods employed by these services:
| Method | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Behavioral Advertising | Targeted ads based on user browsing habits and preferences. | Social media platforms showing ads relevant to recent searches. |
| Data Brokering | Selling aggregated user data to third-party companies. | E-commerce sites sharing purchase history with marketing firms. |
| Subscription Models | Offering a free version with limited features and a paid version with enhanced privacy. | Music streaming services with ad-free premium options. |
Each of these methods underscores a fundamental truth about free digital services: they are not truly free. Users pay with their data, which can be a valuable commodity in the digital economy. This exchange raises important questions about consent, transparency, and the true cost of digital convenience.
As we navigate through the digital landscape, it becomes increasingly important for users to be aware of these hidden costs and to consider the implications of their digital footprints. Understanding these dynamics can empower users to make more informed decisions about the services they use and the data they are willing to share.
Understanding Data Monetization
This section delves into the intricate dynamics of how value is extracted from user-generated content within digital platforms. It explores the transformation of raw user interactions into a commodity that fuels the economic engines of the digital world.
Over the years, the significance of user-generated content has evolved dramatically. Initially, user interactions were merely a byproduct of online activities. However, with the advancement of technology and the proliferation of internet usage, these interactions have become a valuable asset for businesses. The following table illustrates the evolution of the perceived value of user interactions:
| Year | Perceived value |
|---|---|
| 2000 | Minimal; considered as part of user experience enhancement |
| 2005 | Moderate; recognized as a source of market insights |
| 2010 | Significant; integral to targeted advertising strategies |
| 2015 | High; key driver in data-driven business models |
| 2020 | Pivotal; central to digital economy and innovation |
This evolution reflects a shift in how entities view and utilize user interactions. From being a mere enhancement to the user experience, these interactions have transformed into a critical component of business strategies, influencing everything from product development to marketing tactics.
Moreover, the monetization of user interactions has led to the development of sophisticated algorithms and technologies that analyze and interpret this data. These advancements not only enhance the precision of marketing efforts but also create new opportunities for revenue generation. As we move forward, understanding this transformation is crucial for both users and businesses to navigate the complexities of the digital economy effectively.
The Evolution of Personal Information value
In this section, we delve into the transformative journey of the worth attributed to individual details in the digital realm. As technology advances, the significance of these snippets of data has undergone a profound shift, impacting various facets of our digital interactions.
Historical Context: Initially, user details were primarily collected for basic administrative purposes. However, as the digital landscape evolved, so did the methods and motives behind data collection. Today, these details are not just mere byproducts of online activities but are integral assets that drive economic strategies.
Monetization Mechanisms: The transformation of personal details into a valuable commodity has led to sophisticated monetization mechanisms. Businesses now leverage these insights to tailor their offerings, predict consumer behavior, and enhance their marketing efforts, thereby turning individual data points into a lucrative resource.
Market Dynamics: The value of personal details fluctuates based on market demands and technological capabilities. As analytical tools become more advanced, the depth of insights derived from user data increases, thereby escalating its commercial value. This dynamic interplay between technology and market needs continuously reshapes the worth of personal data.
Ethical and Legal Considerations: With the escalating value of personal details comes increased scrutiny regarding ethical and legal boundaries. Regulatory frameworks are evolving to protect user rights and ensure fair practices in data handling. These developments underscore the complex balance between leveraging data for economic gain and respecting individual privacy rights.
In conclusion, the evolution of the value attributed to personal details reflects a broader narrative of technological advancement and economic strategy in the digital age. Understanding this evolution is crucial for both users and businesses navigating the intricate landscape of data-driven economies.
Cybersecurity Threats in the Data Economy

In the current digital landscape, the exchange of sensitive details has become a critical concern. This section delves into the various risks associated with the electronic transfer of confidential data within the economic framework that heavily relies on such transactions.
As businesses and individuals increasingly depend on digital platforms for transactions and communication, the exposure to potential threats has escalated. Malicious entities are constantly evolving their tactics to exploit vulnerabilities in systems, aiming to gain unauthorized access to valuable assets. These assets can range from financial records to proprietary business strategies, all of which can be compromised if adequate protective measures are not in place.
One of the primary concerns is the rise of sophisticated hacking techniques. These methods are designed to bypass traditional security protocols, often targeting weak points in network infrastructures. Phishing scams, for instance, have become increasingly sophisticated, often mimicking legitimate communications to deceive recipients into revealing sensitive information.
Moreover, the proliferation of malware poses a significant threat. Malicious software can infiltrate systems through seemingly innocuous downloads or email attachments, silently collecting data or causing operational disruptions. The impact of such attacks can be devastating, leading to significant financial losses and damage to reputation.
Another critical aspect is the vulnerability of data during transit. As information is shared across networks, it becomes susceptible to interception. Encryption technologies play a crucial role in safeguarding this data, but their effectiveness can vary, and constant updates are necessary to keep pace with evolving threats.
In conclusion, the digital economy is fraught with challenges that require vigilant monitoring and robust security measures. As technology advances, so must our strategies for protection, ensuring that the benefits of digital connectivity do not come at the cost of security and trust.
Privacy Laws and Their Impact on Users

In this section, we delve into the legal frameworks designed to safeguard individual rights in the digital realm. These regulations play a crucial role in shaping the interaction between consumers and the entities that collect and manage their digital footprints.
Overview of Key Regulations
Various jurisdictions have enacted laws aimed at protecting user confidentiality and ensuring that their digital activities are not exploited without consent. For instance, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe sets stringent standards for the handling of user data, emphasizing transparency and user control.
Impact on User Experience
These laws have a profound impact on the everyday user. They empower individuals by giving them more control over their personal details. Users can now expect clear communication about how their data is processed and can exercise their right to access, rectify, or even erase their data from company databases.
Challenges and Compliance
While these regulations are beneficial, they also pose challenges for businesses. Compliance requires significant investment in technology and personnel to ensure that data handling practices meet legal standards. This can sometimes lead to changes in service offerings or even increased costs that may indirectly affect users.
Global Implications
The influence of these laws extends beyond national borders, affecting global operations of multinational corporations. This has led to a more unified approach to data protection, where similar principles are being adopted worldwide, enhancing the global digital rights landscape.
In conclusion, the legal protections in place are pivotal in maintaining a balance between technological advancement and individual privacy. They serve as a cornerstone for fostering trust in digital services and ensuring that users’ rights are respected in the ever-evolving digital world.
How Companies Track and Use Your Data
In this section, we delve into the intricate mechanisms employed by organizations to monitor and leverage user activity. Understanding these practices is crucial for individuals seeking to protect their digital footprint and maintain control over their interactions on the web.
Tracking Mechanisms: Many firms utilize sophisticated tools to observe user behavior. Cookies, for instance, are small files placed on your device that record delete your data from Whitepages browsing history, preferences, and interactions. These data points are invaluable for businesses aiming to tailor their offerings to consumer interests.
Data Utilization: The collected information is not merely stored; it is actively used to enhance marketing strategies. By analyzing browsing patterns and purchase histories, companies can predict future consumer actions and tailor advertisements accordingly. This targeted advertising not only boosts sales but also ensures that promotional content is more relevant to the viewer.
Legal and Ethical Considerations: While the collection and use of user data are widespread, they are not without controversy. Privacy advocates argue that such practices can infringe on individual rights. Consequently, there is a growing emphasis on transparency and consent in data handling. Regulations like the GDPR in Europe mandate clear disclosure of data usage and require explicit user consent for tracking activities.
In conclusion, the tracking and utilization of user data by companies are pivotal in the modern digital economy. While beneficial for personalized service delivery, it also raises significant concerns regarding privacy and ethical data handling. Users and regulators alike must navigate these complexities to ensure a balance between convenience and personal data security.
The Role of Advertising in Data Collection
In this section, we delve into the intricate relationship between promotional activities and the gathering of user details. It’s a critical examination of how the commercial sector leverages digital strategies to enhance their understanding of consumer behavior.
Promotional efforts on the internet are not merely about showcasing products or services; they are sophisticated mechanisms designed to collect valuable insights about audience preferences and habits. This data is then utilized to tailor more targeted and effective promotional campaigns, ensuring that advertisements are not just seen but also resonate with the intended viewers.
The methods employed by advertisers to gather these insights can vary widely. Cookies, for instance, are small files stored on a user’s device that help track browsing activity. This technology allows advertisers to follow a user’s online journey, collecting data on which sites are visited, how long they are viewed, and what actions are taken. This information is invaluable for creating personalized promotional content that is more likely to engage and convert viewers into customers.
Moreover, social media platforms have become rich sources of user data. Through interactions such as likes, shares, and comments, advertisers can gauge public sentiment and tailor their messages accordingly. The integration of advanced analytics tools further enhances this process, enabling advertisers to predict trends and behaviors, thereby optimizing their promotional strategies.
However, the collection of user data for promotional purposes raises significant ethical and privacy concerns. Users are often unaware of the extent of data collection and how their information is used. This lack of transparency can lead to mistrust and reluctance to engage with online promotional content. Therefore, it is crucial for the industry to adopt clear and ethical practices regarding data collection, ensuring that users are informed and have control over their personal details.
In conclusion, while advertising plays a pivotal role in data collection, it is essential to balance the pursuit of commercial objectives with respect for user privacy. Transparency, consent, and ethical practices are key components in maintaining this balance and fostering a more trustworthy digital environment.
User Awareness and Data Protection Strategies
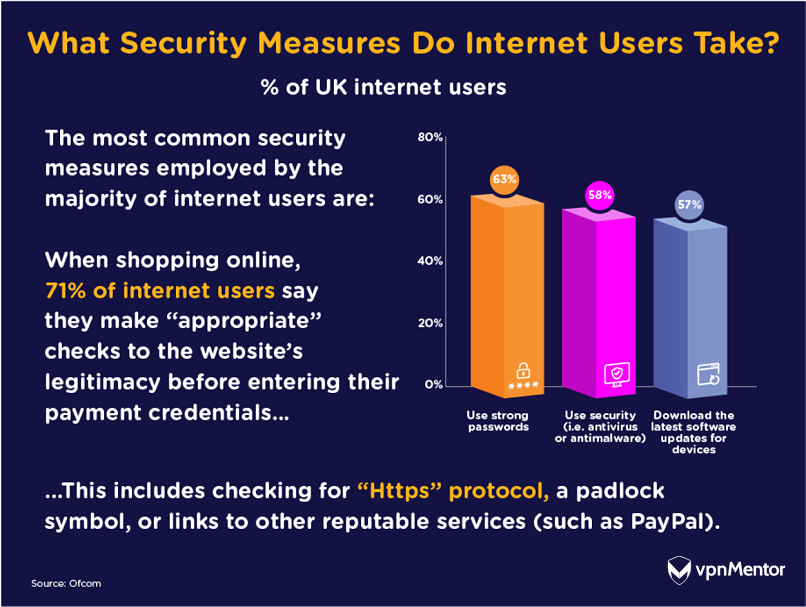
In this section, we delve into the proactive measures individuals can adopt to safeguard their digital presence. As the digital landscape evolves, it becomes imperative for users to understand and implement strategies that enhance their security and privacy online.
Understanding the mechanisms by which entities collect and utilize user data is crucial. Here, we explore various tactics that can be employed to mitigate risks associated with data exploitation. These include simple everyday practices as well as more sophisticated methods that leverage technology to protect personal details.
| Strategy | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Strong Passwords | Using complex combinations of letters, numbers, and symbols to secure accounts. | Reduces the likelihood of unauthorized access to personal accounts. |
| Two-Factor Authentication | Implementing an additional layer of security that requires a second form of verification beyond the password. | Enhances account security by adding an extra step that verifies the user’s identity. |
| Regular software Updates | Keeping all software, including operating systems and applications, up to date. | Fixes known vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors. |
| Data Encryption | Converting information into a code that prevents unauthorized access. | Protects sensitive data from being accessed or tampered with by unauthorized individuals. |
| Privacy Settings Adjustment | Configuring settings on social media and other platforms to limit data sharing. | Controls the amount and type of information shared with third parties. |
By integrating these strategies into daily digital routines, users can significantly bolster their defenses against data breaches and unauthorized surveillance. It is also important to stay informed about emerging threats and changes in data protection regulations to continually adapt these strategies.
The Future of Data Privacy Regulations
This section delves into the intricate balance between the ease of use and the safeguarding of sensitive details in the digital realm. As technology advances, the necessity for robust frameworks to protect user confidentiality becomes increasingly critical.
In recent years, there has been a significant shift towards more stringent rules regarding the handling of user data. These regulations aim to empower individuals by giving them more control over their personal details while also ensuring that businesses operate responsibly.
| Aspect | Current Status | Future Outlook |
|---|---|---|
| Legislation | Various laws exist, such as GDPR in Europe, which set strict standards for data protection. | Predicted expansion of such laws globally, with more specific provisions for emerging technologies. |
| User Awareness | Increasing, but still limited in some regions. | Expected to rise significantly as education and awareness campaigns become more widespread. |
| Technological Solutions | Existing tools like encryption and anonymization are being used. | Advancements in AI and blockchain could lead to more secure and user-friendly solutions. |
The future of data privacy regulations will likely focus on creating a more transparent and equitable digital environment. This involves not only strengthening legal frameworks but also fostering a culture of respect for privacy among both consumers and corporations.
As we move forward, the challenge lies in crafting policies that are flexible enough to adapt to technological changes while remaining robust enough to protect individuals’ rights. This delicate equilibrium will be crucial in shaping the digital landscape of tomorrow.
Balancing Convenience with Data Security
In the modern digital landscape, the tension between ease of use and safeguarding sensitive details is a pivotal concern. This section delves into strategies and considerations necessary to maintain a harmonious balance between these two critical aspects of digital life.
As we navigate through various platforms and applications, the desire for seamless and efficient experiences often clashes with the need to protect our confidential information. Striking the right equilibrium is essential not only for individual users but also for businesses and regulatory bodies.
| Aspect | Convenience | Security |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Refers to the ease of access, speed, and simplicity in using digital tools and services. | Involves measures taken to protect data from unauthorized access or breaches. |
| Examples | One-click purchases, auto-fill forms, and quick logins. | Two-factor authentication, encryption, and regular security updates. |
| Challenges | Can lead to oversimplification, potentially compromising user data. | Overly stringent measures might complicate user experience, deterring usage. |
| Solutions | Implementing user-friendly security features that do not impede convenience. | Educating users about the importance of security measures and how they can be seamlessly integrated into daily use. |
To achieve this balance, it is crucial for developers and policymakers to consider both the user experience and the robustness of security protocols. This involves creating intuitive security features that are transparent and easy to use, without sacrificing the integrity of the data protection mechanisms.
Ultimately, the goal is to foster a digital environment where users can enjoy the benefits of modern technology without compromising their safety. This requires ongoing dialogue and innovation in both the technological and regulatory spheres to adapt to new challenges and user needs.
